Here are the symptoms, causes, risk factors, and complications of Lupus
LUPUS – Known as the systemic autoimmune disease that occurs when the immune system of your body attacks your own tissues and organs, this can affect other systems in the body such as the joints, skin, kidneys, blood cells, brain, heart, and lungs.
Based on the article from Mayo Clinic, this kind of disease is hard to be diagnosed sometimes because its symptoms mimic the symptoms of other diseases. To better understand this health condition, here are the symptoms, causes, risk factors, and complications.
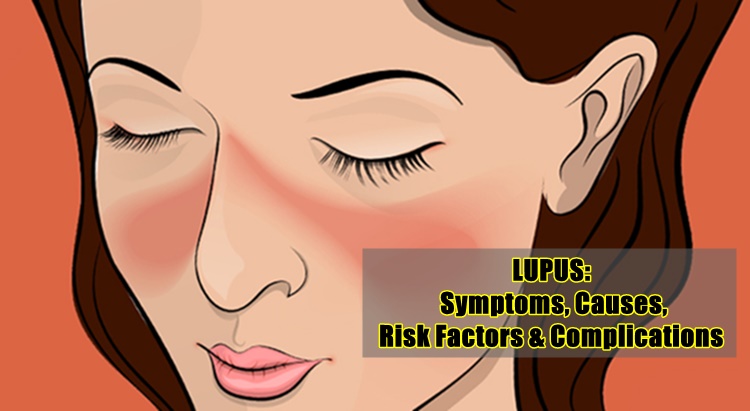
SYMPTOMS
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Joint pain, stiffness and swelling
- Butterfly-shaped rash on the face that covers the cheeks and bridge of the nose or rashes elsewhere on the body
- Skin lesions that appear or worsen with sun exposure (photosensitivity)
- Fingers and toes that turn white or blue when exposed to cold or during stressful periods (Raynaud’s phenomenon)
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Dry eyes
- Headaches, confusion and memory loss
These symptoms depend on which system of the body is affected but the ailment. Based on the article, there are no two cases of lupus are alike, they vary all the time. It can be possible that the symptoms may come suddenly or slowly, mild or severe, temporary or permanent. If unexplained rash, ongoing fever, persistent aching or fatigue develop, consult a doctor immediately.
CAUSES
A person may acquire lupus through the combination of these factors – genetics and the environment. Those who have inherited its predisposition may develop the disease when they come into contact with something in the environment that could be a triggering factor. Here are the potential factors that will trigger lupus:
Exposure to the sun/sunlight may bring on lupus skin lesions. It may also trigger an internal response in susceptible people. Another factor is having an infection that can initiate the disease or cause relapse in some people. In some cases, certain types of blood pressure medications can trigger the disease, as well as anti-seizure medications and antibiotics. Drug-induced lupus may stop once the person will stop taking the medication. Usually, or in most cases, the symptoms will no longer persist after stopping the medication.
RISK FACTORS
Gender, age, and race can be the risk factors for this ailment. Lupus patients are mostly women. Though people of all ages can be diagnosed with this, it is most common for people between the ages of 15 and 45. African-Americans, Hispanics, and Asian-Americans are the most common races that are affected by this, according to the article.
COMPLICATIONS
Here are the parts of the body that can be affected by the inflammation caused by lupus:
Kidneys
– kidney failure or damage that can be fatal
Brain and central nervous system
– headaches, dizziness, behavior changes, vision problems, strokes or seizures
– memory problems
– difficulty in expressing their thoughts
Blood and blood vessels
– blood problems such as anemia and increased risk of bleeding or blood clotting
– inflammation of the blood vessels (vasculitis).
Lungs
– inflammation of the chest cavity lining (pleurisy)
– breathing painful
– bleeding into lungs and pneumonia
Heart
– inflammation of your heart muscle, your arteries or heart membrane (pericarditis)
– cardiovascular disease and heart attacks’ risk increases
READ ALSO: MENOPAUSE: 6 Things That Make Women More Prepared For This Stage
